11 Common Types of Managers in Management and their Roles (Explained)
Types of Managers in Organization
Broadly types of managers differ from organization to organization. They can be categorized on the basis of levels of management, functional area, and nature of the managerial jobs.
Different managers are appointed to the organization based on their area to work and the skills they hold. In management, managers’ types are classified based on three categories and can be of a total of 11 types or more. They are:
- Based on Levels of Management
- Top Level Managers
- Middle-Level Managers
- Lower Level Managers
- Based on Functional Areas
- Marketing Manager
- Financial Manager
- HR Manager
- Sales Manager
- Production Manager
- Based on the Nature of Managerial Job
- Generalist Manager
- Functional Manager
- Staff Manager
Let’s understand the above types of managers in detail.
11 Types of Managers
Explanations of 11 major types of managers are given below:
Based on the Levels of Management
On the basis of the levels of the organization, managers are classified into three subcategories. Based on the levels they have different authority, roles, and responsibilities to fulfill. They are:
Top-Level Managers
The top-level managers hold the top position in the managerial hierarchy. They are also known as the head of the organization.
These managers hold the ultimate power of authority in the organization as such they are responsible to set the overall direction of the firm. CEO, Managing Director, Chairperson, etc. are some examples of these managers.
They do roles like setting long-term plans, policies, and strategies, analyzing the environment, appointing necessary personnel, delegating necessary authority to different organizational units, and directing and controlling the overall activities of the organization.
Middle-Level Managers
Middle-level managers are responsible to look after departmental jobs or middle-level functions of the organization. These managers have the largest number as compared to top managers in the organization.
Related: 10 Roles of a Manager in the workplace
They bridge the gap between top and lower managers in any organization. They receive instruction, guidance, and authority from the top managers and direct lower-level managers and are also responsible to give a progress report to top managers.
Departmental heads like marketing, finance, production manager, etc. are some examples of middle-level managers. They play a significant role as they coordinate between plan makers and actual workers.
Their activities include:
- Assisting in activities of top-level managers and providing suggestions to increase organizational efficiency.
- Formulating middle-level goals for departments.
- Receiving guidance from the top and controlling lower-level managers.
- Building team spirit and managing group efforts in the organization.
Lower Level Managers
Lower-level managers are at the bottom of the managerial hierarchy. They are also called operational or first-line managers. They do the actual daily activities so as to implement plans and policies developed by the above two types of managers.
Lower-level managers’ examples include – supervisors, coordinators, office managers, unit managers, etc. They are responsible to formulate day-to-day plans and policies under departmental goals, assigning tasks to operating employees, arranging different tools to support daily activities, and controlling the activities of operating-level employees
Also Read: 6 Key Managerial Skills
Based on Functional Areas
On the basis of functional areas, managers are assigned specific tasks to perform. They are responsible to do tasks in their respective area as appropriately as possible.
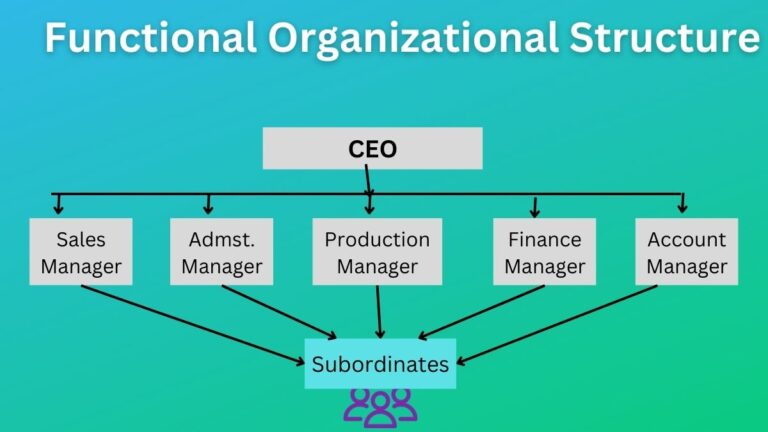
These managers come under the above-explained middle-level managers. Based on the size and nature they differ from firm to firm. From them some 5 common manager types are mentioned below – in addition, there will also be procurement manager, account manager, operation manager, and so forth.
Marketing Manager
The marketing manager is responsible to introduce products in the market and influence the customers. Interacting with customers, building long-term relationships, increasing market reach, etc. are the essential functions marketing managers have to do.
He should make interesting marketing campaigns and market products considering the customer’s preferences.
Financial Manager
The financial manager is one who manages the money materials in the organization. He is strongly responsible for as effectively as possible to collect, managing, and investing money in productive sectors.
He should allocate money where it is needed most. Matching limited money with different units of the organization is a necessary role to perform.
Human Resource Manager
HR manager is responsible to manage people in the organization. He is responsible to hire the right personnel, keep the right personnel, and assign the right tasks to the right personnel.
The right HR planning and implementation are important to increase employee productivity and performance in the organization.
Sales Manager
Sales are through which a company compensates its expenses incurred in the production of goods and services. The sales manager’s duty is to increase sales as much as possible.
His duty is to find the right customers who will actually buy the products. The right and effective sales managers are important to increase the sales of the organization.
Production Manager
A production manager’s duty is to collect raw materials, process them, and make finished goods. He is responsible to produce products that customers like the most.
Related: What is Production Concept?
He should be able to produce products with the sales state of the company i.e. when sales go on increasing he should be able to increase production and vice versa.
Based on the Nature of Managerial Jobs
Managers may also perform different jobs other than the levels and functional areas. Based on the nature of work the manager’s types can also be three – functional, general, and staff manager.
General Manager
A manager who performs different activities in the organization as per the requirement apart from his main duty is called the general manager. They are responsible to solve organizational complex problems whenever arises, they have to shift from time to time to different organization as such they are not specialized in a specific area.
CEOs, Presidents, Vice Presidents, General Managers, etc. come under this category.
Functional Manager
Functional managers are the opposite of general managers in terms of specialization. Functional managers are specialized in specific areas.
They have clear duties, roles, and responsibilities to handle the performance of their respective area. It again comes, all the department heads of the organization are called functional managers. As explained above such as production, sales, finance, public relation, R&D, etc.
Staff Manager
Examples of staff managers are legal advisors, external auditors, management consultants, etc. They are specialized in their field. They directly do not possess a particular position in the organization but play a significant role between functional and general managers for necessary guidance and suggestions.
In Conclusion…
These are some of the common types of managers found in organizations. But these are not all, based on the size, nature, and location of the organization there could be more or less than these 11 types.
Read Next: Qualities of a Good Manager
Sajan Kushmi is a content writer with more than 4 years of experience. He holds BIM Degree. He write on the topics related to Management, Marketing, and Entrepreneurship.





This article really helpful and easy to understand.
You are welcome, Aysha