What is Communication Structure? Definition and 5 Types
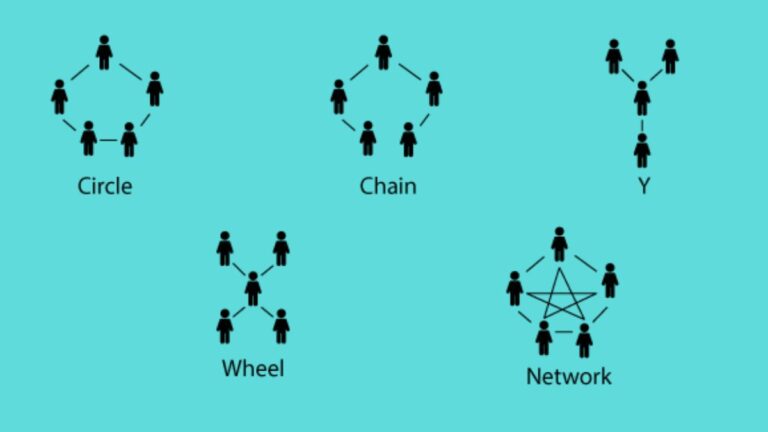
What is Communication Structure? A communication structure is a pattern that is implemented in the organization to maintain the flow of information. It regulates the flow of information within an organization. Communication structure is also called a communication network or communication channel. For the smooth flow of information, different formal communication networks are necessary to…