What is a Multidivisional Organizational Structure? Definition, and, Pros/Cons
What is a Multidivisional Structure (M-Form)?
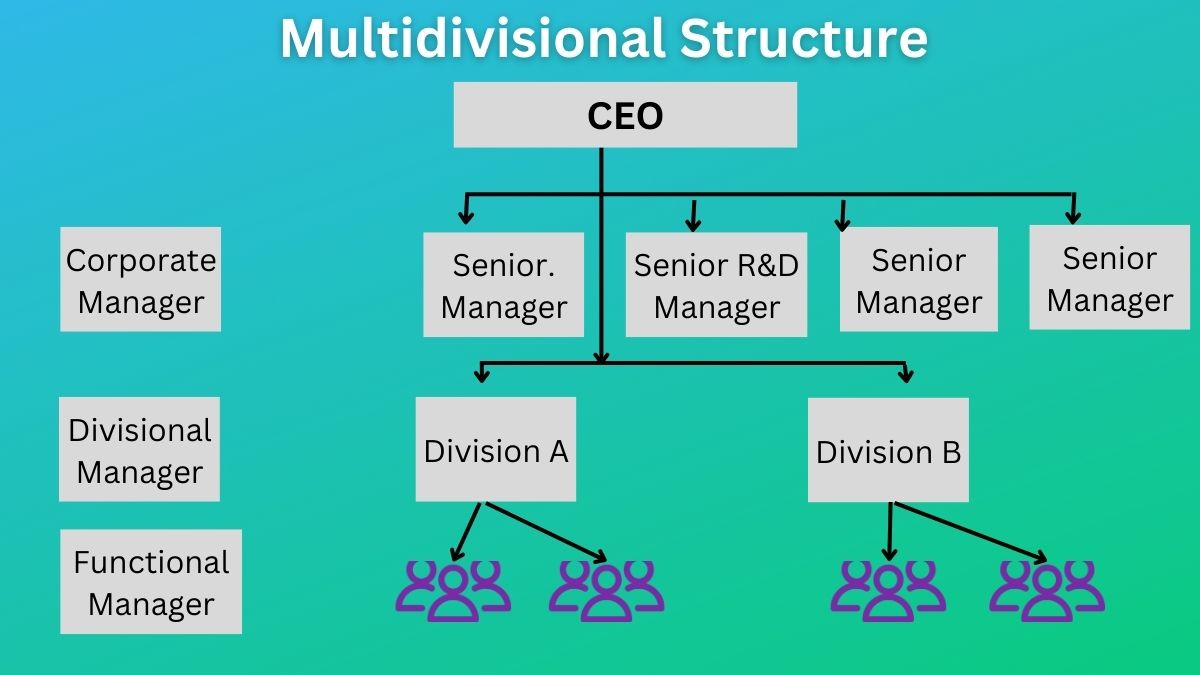
A multidivisional structure, also called M-Form is an organizational structure in which an organization is divided into different product divisions. Each division works independently and is responsible for its performance.
It consists of a complex organizational structure with separate business divisions each working independently. When a firm has different products and operates in a wide range of geographical areas the multidivisional structure is a viable option.
General Electric is a good example that uses M-form organizational structure. It has product divisions such as energy, capital, home & business solutions, healthcare, aviation, and transportation. Similarly, The Walt Disney Company has also followed this and has multiple divisions like television, broadcasting, theme park resorts, streaming media, consumer products, publishing, etc.
Each division of both General Electric and The Walt Disney Company works independently, they are free from other divisions’ responsibilities, however, they are responsible to the general manager, and all are contributing to the overall goal of the organization.
It often confuses us that, the functional and multidivisional organizational structures are the same. But they are different, in a functional organization, the creation of departments occurs at the employee levels, and employees are grouped with similar tasks to increase their working efficiency. And, in a multidivisional organization, the grouping occurs at the functional level itself, and employees are hired within the divisions.
Advantages of Multidivisional Structure
The following are the main pros of a multidivisional organizational structure.
Organizational Effectiveness
In this organizational structure, there is a clear division of work between the top manager and divisional managers. All have clear roles, responsibilities, and authority and work independently. As per the need and situation, they can make necessary decisions for effectiveness. This helps in increasing the organization’s working efficiency and effectiveness.
Related: Geographical Organizational Structure
Helps in Expansion
One of the advantages of a multidivisional organizational system is that it facilitates businesses to expand their operations. It is helpful for big businesses and when applied successfully gives long-term benefits. It helps to create divisions based on the market situation of different geographical areas and ensures the hiring of specialists in such markets.
Creates Portfolio
In this organizational structure, the company expects profits from its all business segments. However, when one business segment faces losses the yield of other segments balances the portfolio of the organization.
Promotion
In this organizational structure, in most cases, the most competent divisional managers are promoted to corporate managers. So, the morale of divisional managers is boosted.
Creates Synergy
All the divisional units of the organization work together towards the same final target which creates synergy in the organizational operation. It is the result of the effective management of different divisional team members.
Disadvantages of Multidivisional Structure
Despite many pros, a multidivisional structure also has its cons. Some are mentioned below:
Poor Coordination
One of the disadvantages of the multidivisional system is that there is poor coordination between divisional managers. They do not give value to other divisional managers. Since they are given too much autonomy they are too focused on their business area and ignore the other segments of the organization.
Costly Structure
This is also a costly organizational structure and can not be suitable for small-sized organizations. Organizations adopting multidivisional organizational systems have to invest more money in divisional managers’ services and new investment projects, which results in asking for more money from the top management.
May Compete For Scarce Resources
There might also be a condition when different divisional managers request financial assistance but because of the scarcity of finances in the organization, the divisional managers may compete with each other. This even creates conflict between the divisional units.
Too Much Autonomy
A divisional organization could lead to each division feeling overly autonomous. Each division may consider itself to be entirely independent of the other divisions and become more focused on achieving its own goals than the goals of the organization as a whole.
The inability to achieve the organization’s overall goals and operate at its highest levels of efficiency may be the outcome of poor leadership in such an organization.
Read Next: Matrix Structure
Sajan Kushmi is a content writer with more than 4 years of experience. He holds BIM Degree. He write on the topics related to Management, Marketing, and Entrepreneurship.






How to escape the matrix