What is Organizational Development (OD)? Definition, Objective, Features, and Process
What is Organizational Development (OD)?
Organizational development, commonly known as OD is a systematic and planned process of changing an organization’s plans, policies, processes, and strategies to be more effective and efficient. The main goal of OD is to increase the overall growth of the organization.
OD focuses on continuous improvement in the company’s culture, strategies to deal with new opportunities in a positive way, and encourages employees to be more open to accepting change so as to increase the organization’s performance.
Organizational development is a science-based yet humanized approach to bringing change to the organization. It involves a systematic long-range process of making organizations effective and adaptive to environmental changes by developing, improving, and reinforcing strategies, structures, and processes of the firm.
Objectives of Organizational Development
The goal of organizational development (OD) is to support organizational performance by coordinating the structural, cultural, and strategic aspects of work to meet the demands of a constantly changing business environment.
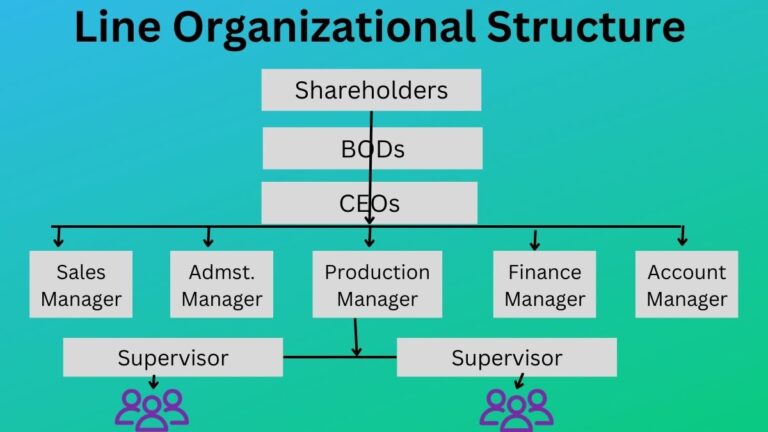
Related: Organizational Structure
Using a comprehensive and humane approach that places people at the center of the process, OD fosters transformation in organizations. The following are the main objectives of OD.
- Improve the performance of the organization.
- Develop efficiency and effectiveness.
- Continuous improvement.
- Make organizations adaptive to change.
- Bring change through employee development.
- Increase the productivity and profits of the organization.
- Encourage organizations to be competitive in the changing business climate.
Characteristics of Organizational Development
The following are the main features of OD.
Ongoing Process
OD focuses on the ongoing improvement of organizations’ processes, systems, and strategies. OD believes the business climate is ever-changing, as such, to be competitive here organization should make continuous improvements in its operations.
Related: PDCA Cycle
Long-Term Focus
OD is a deliberate strategy to control change in the workplace. It emphasizes a long-term strategy to raise the organization’s operational effectiveness.
Dynamic Process
OD is a dynamic process that can be changed depending on the situation. To change its systems and practices, a significant amount of money and effort are required. Up to the organization’s operation, the process is continual and collaborative.
Research-Based
Research and experimentation are the foundation of OD interventions. Experts in organizational development gather data and information, analyze it using applicable methods, and make decisions.
Collaborative Approach
OD emphasizes collaboration and group work. It explains that a participative approach would be a strength for an organization to achieve the desired goals.
Process of Organizational Development
OD is a systematic, continuous, and complex process. The following are its main steps.
Identify the Problem
The process of OD begins with identifying the area of the organization where the change is needed. Usually, it is done by top management. Management should ask itself what is the problem, what the change is, and why it is necessary.
Collection of Information
Once the problem is identified, management should collect the data and information related to the problem. The collected information should facilitate the analysis of the problem.
Related: Planned Change Process
Feedback
In this stage, the information is analyzed and a summary of the analysis is made. The summary then is provided to different organizational members to get their feedback on whether or not the information is desirable to solve the problem identified in Step 1.
Develop An Action Plan
An action plan is needed to prepare to solve the problem. Management should develop different alternatives, analyze them, and come up with the most appropriate alternative to solve the problem.
Implementation
Once the action plan is developed the next step in the OD process is to implement it in the real field. Management should define everyone’s role in it so as to make the implementation successful. If necessary the manager should consult, assist, and instruct the employees.
Evaluation
As it is said, OD is a continuous process, the review should be done to know the impact of the OD process on organizational performance and its effectiveness. Here, the change outcome is assessed to determine whether the initiative meets the goal or not.
Values of Organizational Development
In addition to the science-backed approach, OD is also a humanistic and social approach. OD emphasizes building good relationships between management and employees before initiating the change. The following are the key OD values identified in Robbins, 2003p. 553.
Respect For People
People i.e. employees in the organization should be treated well with dignity and respect. They are key to bringing change in the organization and improving its performance. They are responsible and caring and when they are treated well the work can be done flawlessly.
Trust and Support
Without trust and support for each other, the organization would not be able to walk for longer. Trust, authenticity, openness, and a supportive climate are the main characteristics of a healthy work environment.
Power Equalization
Organizational development explains that effective organizations de-emphasize the practice of hierarchal authority and control.
Confrontation
Transparency should be in the organization. Management should openly confront the problems. Everyone should be aware of the problem and given a chance to minimize or eliminate it. Transparency in activities increases the interest of employees.
Participation
OD also values the practice of participative management in the organization. The manager himself only should not decide about the change, employees should also be invited to discuss it. It is said that employees who will be affected by the change if they are involved in decision-making will be more committed to implementing such change decisions.
Read Next: Strategies to Manage Resistance To Change
Sajan Kushmi is a content writer with more than 4 years of experience. He holds BIM Degree. He write on the topics related to Management, Marketing, and Entrepreneurship.