Planning in Management: Definition, Objectives, Features, Process, Principles, Types, and Importance
Suppose your goal is to get +90% marks in your coming examination. Your goal is set, Now what you need to do is to decide how to (read) prepare, what to read, whether to take tuition or not, self-read or ask for help from seniors, etc. All you have to do is to be prepared to successfully get +90% marks. For this, what you are doing, you are planning i.e. you are deciding beforehand activities so that you can successfully achieve the +90% marks i.e. your goal. The same happens in organizations.
Here, we will discuss what planning is, its features, objectives, how to make plans, principles, and its importance in an easy yet insightful way.
What is Planning?
Planning is the process of deciding on necessary activities to be done today so that the desired goals can be achieved as expected. It is the action that bridges the gap between where we are now and where we want to be.
In a simple sense, planning is making plans in advance on what is to be done and how it is to be done. It includes setting organizational goals and objectives and choosing various activities to ensure the achievement of those goals and objectives as effectively and efficiently as possible.
Planning is the first and one of the foundational functions of management. It is not more but an act to think before taking an action. It is also called an action to choose the best one from the pool of choices.
It is an effective tool to ensure an organization’s desired goals are achieved. Managers have to make effective plans to make the company’s goals gain in an efficient manner. Effective plans help to convince the employees and motivate them to give their highest effort.
Planning in management is not just to see the future but also to shape the future of the organization. It reduces uncertainty in implementation, increases efficiency, and provides an effective direction to get the intended outcome. Every manager must strive to make a plan that is precise, measurable, achievable, logical, and time-specific.
What is the Objective of Planning?
Planning is critical for organizational success, growth, and survival. It is the roadmap of an organization that depicts a way and how the organization has to walk on it to get its desired outcome i.e. goal. The following are its main objectives:
- Ensure the achievement of organizational goals and objectives.
- To provide effective direction to invest organizational efforts.
- Reduce uncertainties that a firm would face in the future.
- Brings the economy into operation.
- Increase organizational efficiency.
- To reduce the failure rate of plan implementation.
- Helps to see the future and be ready to take action.
Characteristics of Planning
Planning is defining the organizational goals, establishing an overall strategy for achieving those goals, and developing a comprehensive set of plans to integrate and coordinate organizational goals – Robins and Coulter. The following are the common features of the planning function of management.
Goal Focused
Organizational plans are focused on organizational goals. It clearly states the necessary courses of action to achieve the desired goals. For this, it scans the environments, analyzes possible means to achieve goals, selects the most promising one, and implements it successfully.
Primary Function
Planning is the primary function of management and after it, other functions (organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling) come to play.
Pervasive in Nature
It is not like if the top managers make plans and other subordinate managers do not have to care about making plans. It is pervasive in nature i.e. all levels of managers (top, medium, and lower) have to make some plans in the workplace based on their power and responsibilities.
Continuous Process
Planning is not only a process rather it is a continuous process. Till the presence of the company managers continuously have to make different plans. In addition, once one goal is achieved, for the achievement of the next one making necessary plans is necessary.
Future-Oriented
One of the characteristics of planning is that it is future-oriented. Plans are prepared in the organizations for future courses of action. Their main motive is to chase future uncertainties.
Intellectual Activity
Everyone can not make effective plans. For effective plans, the intellectual capacity of plan makers or managers is needed. It needs vision, wisdom, foresight, imagination, and intelligence.
Decision-Making
Since decision-making is the selection of the most feasible option from many. Managers also have to select the same while creating different plans.
Steps in the Process of Planning
How do make a plan in the organization? You or managers should make an effective plan that is appealing, feasible, acceptable, and understandable by all the members of your organization. The plans should convince the employees instead of bringing confusion to the workplace.
The following are the common steps for making organizational plans.
Scan The Environment
At first, managers should scan the environment i.e. the inside and outside environment of the organization. He should be able to identify the strengths and weaknesses of his organization and probable threats and opportunities that come from the external environment.
Set The Desired Goals
In the second step, the manager should be able to set the desired goal that matches the organizational internal strengths and the probable opportunities. The goals or objectives should be specific, clear, and practical.
Determine Premises
Premises are assumptions about the future and are based on future possibilities. Managers should define some premises upon which the plan will be implemented.
Determine Alternatives
Alternatives are the choices a manager can make to achieve the desired goals. There can be many alternatives relating to the desired goals. Managers should develop different alternatives by their experience and the support from the experts.
Analyze the Alternatives
In this step, a manager should analyze the different alternatives based on their cost, benefits, feasibility, risks, chances of achieving desired goals, and effectiveness. He should realize an effective analysis of all alternatives support in the selection of the right one.
Select The Best Alternative
After alternative analysis, a manager must choose an alternative or option that has a greater rate of organizational goal achievement. He must ask a question himself “Whether or not the selected alternative ensures the goal achievement?.”
Develop Supportive Plans
Once the best option is selected, the manager also needs to set supportive or action plans that support the main plan. These action plans may include the formulation of policies, rules, schedules, and budgets.
Implement the Plan
Only making a plan is not enough to attain the desired goals, unless the plan is implemented. Managers should communicate with all employees and provide the necessary guidance to effectively implement the plan.
Reviewing
Reviewing the implemented plan is the last step in the planning process. It is an action taken to know whether or not the implemented plan is working. If necessary, it helps to take corrective actions to ensure the right direction of the plan’s progress.
Principles of Planning
These principles are also called the principles of effective planning. It is said that “a well-designed plan is half completion of the task.”
Related: The 14 Principles of Management
That means if we prepare the plans appropriately, half of the total tasks get completed by themselves. It is critical that every manager should create well-designed or effective plans.
For effective plans, experts have suggested some principles that are worth considering. Let’s understand them shortly.
- Contribution To Objectives – By this principle, the plan that is made should contribute to the achievement of organizational desired goals and objectives.
- Management Interset – Managers are the ones who make the plans, they should be interested in making plans. Their interests have a significant influence on the effectiveness of plans.
- Premises – These are the assumptions about the future likely events. Plans should be based on some premises.
- Primacy – Plan is the first function of management. Plans should be made first because without a proper plan, other management functions can not get the direction.
- Efficiency – This principle states the plans should be made in a way that ensures the goal achievement with minimum efforts and costs.
- Flexibility – The plan should be flexible enough to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Navigational Change – The manager should continually focus on plans, their implementation, and their progress, and review, if necessary bring changes.
- Commitment – The commitment principle is that logical planning encompasses a period of time in the future necessary to foresee, through a series of actions, the fulfillment of commitments involved in a decision today.
- Timing – According to the timing principle of planning, the important ones and less important ones or major and minor plans should be arranged in a time hierarchy.
- Pervasive – All managers should make necessary plans according to the need, power, and responsibilities they hold.
- Alternative – For effective plans planning should be through the selection of alternatives.
- Limiting Factor – An organization may have some limiting factors (e.g. limited resources), and managers must tackle such issues to ensure the effective realization of ultimate goals.
- Comparative Strategies – Managers should also consider the strategies of competitors while setting plans.
- Cooperation – All the members of the organization should cooperatively participate and collectively make the plans.
- Framework – It refers to organizational policies that should be in favor of inclusivity in the workplace.
- Long Range View – Managers must carefully analyze all the available data and plan decisions after thoroughly analyzing and comprehending their long-term future impacts.
Types of Planning
There are five types of plans found in organizations. These include.
- Plans Based on Hierarchy – Hierarchal plans are based on the authority and responsibilities of employees in the organization. They are drawn at three major hierarchal levels, they include strategic plans, tactical plans, and operational plans.
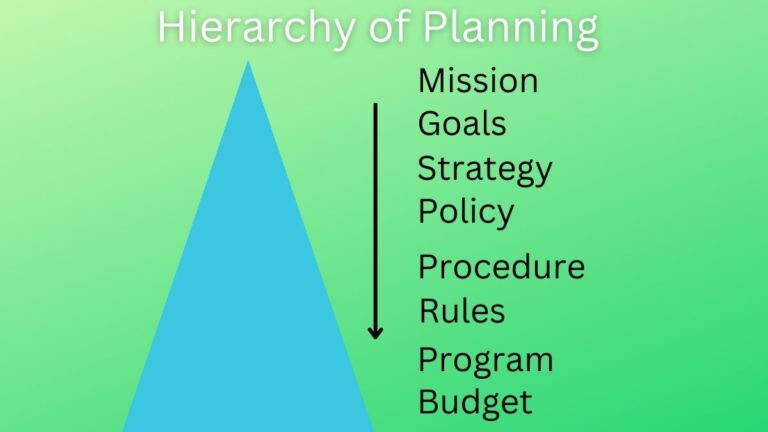
- Plans Based on Frequency of Use – Some plans are used regularly whereas some are only once. Based on frequency plans are single-use plans and standing-use plans. Single-use plans include budgets and programs whereas standing-use plans include goals, strategies, procedures, policies, and rules.
- Plans Based on Flexibility – Based on the extent the plans can be modified or remain static including two specific plans and flexible plans. Specific plans are once made and can not be modified later whereas flexible ones will be modified according to needs.
- Plans Based on Time Frame – According to time frame plans include long-term plan (more than five years), medium-term plan (less than four years), and short-term plan (less than one year).
- Contingency Plan – A backup strategy developed in the event that the primary course of action is unexpectedly interrupted or considered inappropriate is known as a contingency plan, also known as a situational plan.
Importance of Planning
A successful plan lays out a clear road map for achieving such targeted organizational goals which are required for their successful accomplishment. A better strategy will probably result in the outcomes being attained for the least amount of money and effort.
After reading all the above explanations you may have understood why planning is important. In addition, some importance of planning can be mentioned below:
- It provides direction to organizational efforts and activities.
- Ensure the achievement of organizational goals.
- Helps to reduce future uncertainties.
- Decreases the chances of risks.
- Effective utilization of organizational resources.
- Efficient and economic operations.
- Brings coordination.
- Encourage innovative ideas.
- Ensure effective control.
- Reduces business failure.
- Improves organizational performance.
- Helps to identify opportunities and threats.
Presence of effective planning is unavoidable in every organization for smooth functioning and timely goal achievement. It is not necessary but a compulsion for every organization as well as manager to set effective plans.
In Conclusion…
Hence… we can say that planning is all about setting goals and deciding, selecting, and evaluating the alternatives in advance to ensure the desired organizational goals are achieved. And, every organizational member should contribute to developing effective plans.
Read Next: Organizing Function: The 2nd Function of Management
Sajan Kushmi is a content writer with more than 4 years of experience. He holds BIM Degree. He write on the topics related to Management, Marketing, and Entrepreneurship.